-
Mensaje Vacaciones carrito
We're going on vacation!
From August 9th to 24th (inclusive), we’ll be taking a short break to recharge our batteries. Orders placed during this period will be processed as soon as we're back.
Have a great summer! - Healthcare professionals area
- Distributors area
-
Products
Lit-Control ® pH Balance37.40€Lit-Control ® pH Up37.40€Lit-Control ® pH Down37.40€Lit-Control ® pH Meter 2.0199.99€Lit-Control ® pH Buffer9.99€Lit-Control ® pH Sensor99.99€Theobromine22.00€
- Blog
- Our commitment
- Contact
La promoción se te aplicará automáticamente en el último paso del proceso de compra
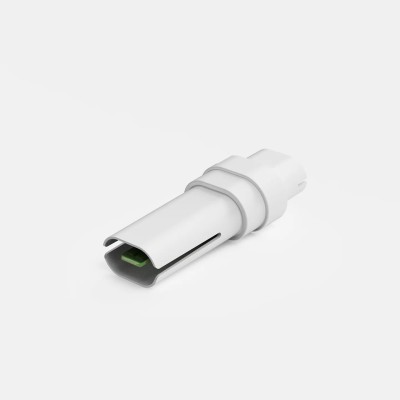
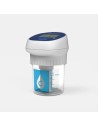
Lit-Control ® pH Buffer
Do you have a Lit-Control® pH Meter 2.0? This calibration liquid is necessary for the correct measurement of your urinary pH. Lit-Control® pH Buffer includes 4 calibration solutions, designed for 4 months of accurate urinary pH measurements.
Remember to replace the calibration fluid with a new one once a month!
-10%
-15%
Summer sales
- *5€ discount on orders over 50€, and 12€ discount on orders over 100€.
- *Promotion valid until 22 July or end of stock.
- *Offer cannot be combined.
We're going on vacation!
From August 9th to 24th (inclusive), we'll be taking a short break to recharge. Orders placed during this period will be processed as soon as we return.
Have a great summer!
Black Friday campaign
10€ off with a minimum purchase of 25€!
Promotion valid online, applicable only once per registered user. Not combinable with other offers.
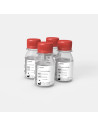
For correct measurement of urinary pH, it is necessary to change the calibration solution once a month.
This product contains 4 calibration solutions so it will last for 4 months.
LT0275.00
9984 Items
1. Dispose of the contents of the old calibration solution in cup ‘C’ down the drain.
2. Pour the contents of a new calibration bottle into beaker ‘C’.
3. Insert the sensor into the new calibration solution that you have poured into beaker ‘C’. Now you can continue your pH measurements as usual!
4. Remember to change the calibration solution for a new one once a month!
• 4x Calibration solution bottles
How to keep the calibration solution in good condition? 



In order to keep this solution in proper condition for as long as possible, it is advisable to follow these precautions:
1. Note the date of first use; after one month replace the calibration solution with a new one.
2. Keep the beaker with calibration solution screwed to the device during storage.
3. Store the calibration solution between 5°C and 45°C.
4. Avoid direct exposure of the calibration solution to sunlight.
How to calibrate the first time you use the device? 



1. Unscrew the beaker and pour in the calibration solution.
2. Screw the cup back onto the device.
.3. Gently shake the device for 5 seconds.
4. Press the button until the device turns on and wait for the ‘C’ symbol to appear on the display. display.
5. Press the button once for calibration to begin.
For the duration of the calibration, a moving dot will be displayed below the symbol. Wait for a few seconds, if the calibration is successful, the ‘T’ symbol will be shown on the display.
What is urinary pH? 



Urinary pH is an indicator of the acidity or alkalinity of urine and provides information about the overall health of the body. general state of health of our body. The average pH value is around 6.2. However, due to its However, due to its oscillating behaviour it can range from 4.5 to 8, depending to a large extent on the diet, waste products, metabolic disturbances, and other causes.
How is urinary pH currently monitored? 



There are currently two options for urinary pH monitoring: by test strip or by laboratory pH meter. laboratory pH-meter. The former are widely questioned by the medical community for their low accuracy and fiability for clinical decision making; while the latter lacks the portability of a pH meter. fiability for clinical decision making; while the latter lacks the portability necessary for urinary pH necessary for the measurement of urinary pH to be made in freshly voided urine, which has fisiological value. fisiological value.
How can urinary pH affect the formation of kidney stones? 



• If crystals are present in the urine and the urinary pH is above 6.2, conditions are suitable for the formation of infectious or calcium phosphate, or calcium phosphate-induced calcium oxalate stones. If crystals are present in the urine and the urinary pH is above 6.2, conditions are suitable for the formation of infectious or calcium phosphate, or calcium oxalate-induced calcium phosphate stones.
• If crystals are present in the urine and the urinary pH is below 5.5, conditions are suitable for the formation of cystine or uric acid, or uric acid-induced calcium oxalate stones. If crystals are present in the urine and the urinary pH is below 5.5, conditions are suitable for the formation of cystine or uric acid, or uric acid-induced calcium oxalate stones.
• On certain occasions, or without pH alteration, the simple existence of crystals and the lack of fisiological inhibitors of this crystallisation, can favour the formation of kidney stones. In certain cases, or without pH alteration, the simple existence of crystals and the lack of fisiological inhibitors of this crystallisation, can favour the formation of kidney stones.
Correct control of urinary pH will reduce the risk of kidney stone formation.
How can urinary pH affect urinary catheters and urinary catheters? 



After placement of a bladder catheter or double j catheter, a urinary tract infection tends to develop, which in most cases can lead to alkaline urine. If the infection persists due to, among other things, the presence of crystals in the urine and an alkaline pH, it may lead to calcification of the catheter or catheter, even obstructing it and in some cases making it difficult to remove.
You might also like
7 other products in the same category:
What our patients say
“Well, I am prone to kidney stones and these capsules help me with maintenance and along with drinking plenty of fluids I haven't had to go to the urologist anymore.”
Nuria
“I use it to prevent the formation of kidney stones.”
Alex
“I have been taking it for two months, my surgeon recommended it to me. I had 3 operations when I was 38 years old and since I've been taking it I haven't suffered any more cramps or swelling and as for the effect I urinate more frequently and better. I had my stones removed by lithotripsy, but they don't seem to form anymore.”
Yohanna
What our patients say
“Great product, good quality.”
Sonia
“I use it to raise the pH of the urine and prevent the formation of kidney stones, I have been stone free for four years.”
Pedro
“So far it works. Better to be safe.”
Miguel
What our patients say
“Since I started taking Lit-Control® pH Down 4 years ago, I have not been in the operating room for stone formation and have not had any problems with urinary obstruction. Bless the hour! With this treatment I have had an excellent result, I am eternally grateful.”
Rafael
“It was sent to my mother by her urologist to control her urine pH and she is doing very well.”
Loli
“They really lower the pH of the urine. They have solved my problem of repeated urine infections. The urologist prescribed them to me and he was right. I had been dragging the problem for 8 months and after three days of taking them I improved dramatically”.
Montserrat
“I have had kidney stones since I was seven years old. Since 2011, I had an operation every two years. And since 2016, several times a year an operation. Since I have these tablets I have not yet needed an operation. I use it since 2 years 2 times a day 1 tablet.”
Danielle
What our patients say
“I just had my first child and during postpartum I suffered from urinary incontinence. Being very prone to urinary tract infections, I use Nodorin which I apply directly to my pad every time I change it to avoid urinary tract infections.”
María
“Two years ago I had a stroke which caused me to have incontinence problems in my bladder. Now I have to wear diapers and since I can't change them as often as I would like, I use Nodorin®. I'm no longer worried about bad odors when I'm with my friends and I can have a better social life!”
Almudena
“As the years go by, I find myself more and more conditioned by urinary leakage: a cough or a laugh can become my worst enemies... with Nodorin, I no longer fear the bad odors or the risks of infections associated with urinary leakage.”
Josefina
“During my menstrual cycle I had the feeling of having unpleasant odors that others could smell too, since using Nodorin I no longer smell anything and I feel more comfortable and self-confident.”
Ana
What our patients say
“We have tried other products, both my husband and I, and none have given us as good results as this one. Even for washing hemorrhoid area.”
Maider
“I have been using it for a week and the truth is that it is a marvel. After trying other similar products that didn't help me at all, this one will undoubtedly be with me for a long time. The sensation after use is one of absolute cleanliness and freshness that is maintained throughout the day, eliminating any feeling of irritation or discomfort. It has a pleasant smell and is respectful to the skin, so far a 10.”
Jaime
“It makes me feel more comfortable since the discomfort that I had been dragging for some time has disappeared, and it also leaves a pleasant feeling of freshness. I also use it with my little daughter and I am delighted. Highly recommended.”
Luz
“It is a gel that I buy for my father, who due to prostate problems must self-catheterize every time he wants to urinate and the urologist told me that he will use these types of gels and wash well, before self-catheterizing, to avoid infections.”
Yolanda
What our patients say
“Since I started taking Metiofitina in June 2024, I went until December of that same year without a single urinary tract infection and without needing any antibiotics. That’s six months of relief, whereas before, I was getting infections every month and a half or two months — increasingly frequent, more intense, and with antibiotics becoming less or completely ineffective against the infection, while causing more and more side effects on my body.”
Miguel
“My urologist recommended this product for me to take along with the antibiotic for a urinary tract infection and the truth is that it has worked very well, in a few days I no longer had an infection! Other times I have had urinary tract infection it has been hard for me to get rid of it just by taking the antibiotic.”
Alexia
“It was recommended to me by my doctor because I have recurrent infections. I've been taking it for months now and I've noticed that if I take it at the slightest discomfort, the infection doesn't get out of control. I'll keep buying it!”
Julia
“I am 25 years old and have had urinary tract infection problems since I was a teenager. A month ago my doctor recommended this product and since then I have had no more problems. I have finally found an effective solution, highly recommended.”
Marcos
“I bought it because I suffer a lot from infection. Within 48 hours the antibiotic had taken effect (much faster than on previous occasions) and the discomfort was gone. It does what it states.”
Andrea
What our patients say
“My urologist has prescribed Canoxidin, to avoid complications with my catheter until the day of my lithiasis intervention. The tablets are small and take well. Now to wait for the operation.”
Miguel
“Canoxidin was prescribed by my urologist to treat the calcification problem of a device I have in place. I have full confidence in Devicare Laboratory products, as, I have already used other products from them and they have more than met expectations. I recommend it 100%.”
Celia
“I am an indwelling catheter patient due to a disease in one of my kidneys. I am awaiting a transplant and the doctor has recommended using this product.”
Marieta
What our patients say
What our patients say
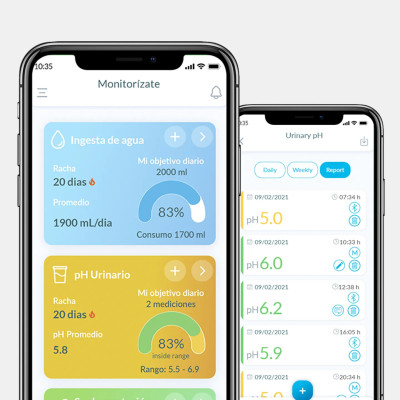
“The device was very helpful to me in adjusting my diet. You can do quick checks from home to know what foods affect my pH and in what way. Thanks to this system I have been able to create my own diet to keep my pH in range.”
Miguel
“This is a very practical product for measuring urine pH: It is very easy to use, the mobile app is an interesting addition to keep track of your daily PH and very good quality.”
Gonzagar
“I am a urinary catheter user due to an injury. To say that it is a reliable device that provides me with the information to keep my PH under control. Therefore, a device that I recommend.”
Rafael
What our patients say
Lit-Control ® pH Sensor
Nombre
Lit-Control ® pH Sensor
Nombre
Lit-Control ® pH Sensor
Nombre
What our patients say
“A year ago I had a urostomy and since then I didn't leave the house or live a normal life. Thanks to this consultation I have regained strength and I see the light.”
Marta
“The communication has been great and the process to do the online consultation very easy. In addition, she has helped me with very useful tips in my day to day life.”
Francisco
“My father has had a stoma for 5 years. It has always given us problems with infections among other things. It has helped me understand how to clean it and what products to use to take care of it to avoid them. I recommend it!”
Julia
What our patients say
“Barbara is a great professional. I have been able to talk to her calmly and she has understood me perfectly, she has explained everything in detail and has prescribed a personalized diet for me, so far I have not had kidney stones again.”
Carla
“After having 3 episodes of renal colic in less than two years, I decided to find solutions. My doctor recommended me to look for a specialized nutritionist, and the truth is that Barbara has delighted me. Since I started with her guidelines, I have been free of kidney stones for more than a year.”
Mª José
“I am delighted! I now know what I should eat and what foods I shouldn't abuse. I feel empowered with my health 😊”
Laura
“Very professional! She adapted perfectly to my situation and explained everything in detail so I could understand. I would definitely recommend her.”
Pedro
What our patients say
“After I started taking Savebone®, I noticed an improvement in my energy and I feel stronger. It’s a relief to know I’m taking care of my bones with something that works!”
Ana María
“Since I started taking Savebone®, I’ve noticed a significant improvement in my well-being. My bones feel stronger, and I no longer have that feeling of fragility that used to worry me. I totally recommend this supplement!”
Isabel
“I’ve been using Savebone® for several months, and my doctor has told me that my calcium levels have improved significantly. Now I feel more confident and active. This product has given me the confidence I needed to take care of my bones.”
Laura
“I used to suffer from joint pain due to low bone density, but after using Savebone® for a few weeks, I’ve noticed an improvement. My bones feel stronger and my movements are smoother. It’s definitely part of my daily routine now.”
Maria
“I’ve tried many supplements to strengthen my bones, but Savebone® is the only one that has truly given me results. I feel more at ease knowing I’m taking something backed by research and made with quality ingredients.”
Carmen
We recommend you
Stay up to date with the latest news!
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive news,
promotions and related news.